We have cooperated with more than 200 countries in solar energy projects and road lighting projects. We have exported products to many countries and participated in many important government projects around the world.

An MPPT solar inverter (Maximum Power Point Tracking solar inverter) is a power conversion device that continuously adjusts the operating voltage and current of photovoltaic (PV) panels to ensure they operate at their maximum power point under changing sunlight and temperature conditions.
Compared with basic inverters or PWM-based controllers, MPPT solar inverters can increase real-world energy yield by approximately 10–30%, especially under partial shading, variable irradiance, or high-temperature environments. Modern MPPT inverters may feature single or multiple independent MPPT channels, enabling flexible PV string design and reducing mismatch losses.
In hybrid configurations, MPPT hybrid inverters integrate solar power conversion, battery charging and discharging, and grid interaction into a single system, allowing seamless operation in grid-tied, off-grid, and weak-grid scenarios. Due to higher efficiency, improved system stability, and better long-term return on investment, MPPT inverters have become the industry standard for residential, commercial, and energy storage solar systems worldwide.
An MPPT inverter (Maximum Power Point Tracking inverter) is a solar inverter that continuously adjusts the operating voltage and current of photovoltaic (PV) panels to extract the maximum available power under changing environmental conditions.
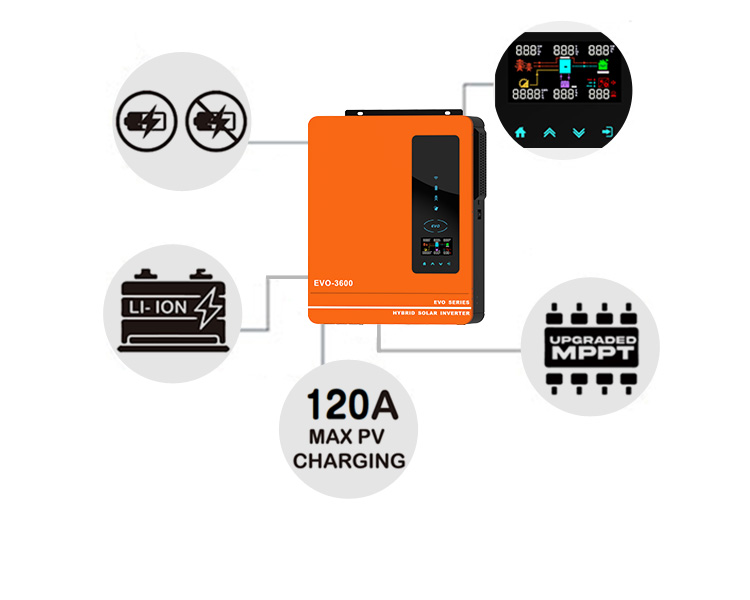
A solar inverter with built-on MPPT controller
You may also see it referred to as:
MPPT solar inverter
Inverter with MPPT
MPPT solar charge controller inverter
Hybrid MPPT solar inverter
MPPT Solar Converter
Although the names vary, the core idea is the same:
MPPT allows the inverter to intelligently match the PV array's optimal power point instead of forcing panels to operate at a fixed voltage.
From a system perspective, an MPPT solar inverter integrates:
l MPPT solar charge control
l DC–AC power conversion
l Battery charging and discharging (for hybrid systems)
l Grid and generator interaction
In practical terms:
MPPT inverter = high-efficiency DC–AC conversion + intelligent maximum power tracking
Key Advantages
l Seamless grid-tied and off-grid operation
l Optimized battery utilization
l Strong adaptability to unstable or weak grid environments
MPPT stands for Maximum Power Point Tracking.
In a solar inverter, MPPT is not a standalone component, but a combination of:
Control algorithms
Power electronics (typically DC–DC converters)
Real-time sensing and feedback systems
The core functions of MPPT include:
Tracking the optimal voltage–current operating point of PV modules
Dynamically responding to changes in irradiance, temperature, and shading
Increasing usable energy output compared with non-MPPT systems
In real-world operation conditions, MPPT typically improves energy harvest by 10–30%,depending on climate, system design, and load profile.
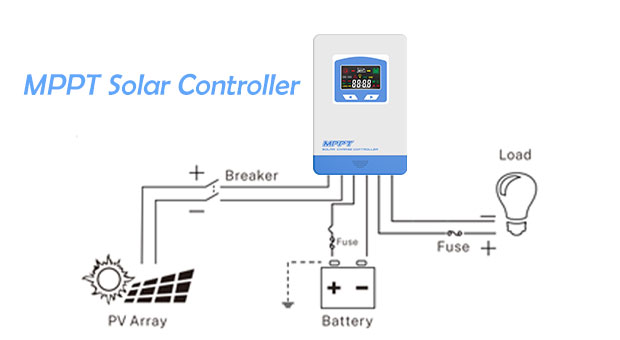
An MPPT inverter operates through a high-speed closed-loop control process, consisting of the following steps:
1. Sampling
Continuous real-time measurement of PV array voltage and current.
2. Power Calculation
Instantaneous power is calculated using the relation:
P = V × I
3. Algorithmic Decision
The embedded MPPT algorithm (such as the Perturb and Observe method) compares current and previous power values.
4. Operating Point Adjustment
Based on algorithm output, the inverter adjusts the switching behavior of the DC–DC conversion stage (e.g., Boost or Buck-Boost circuits), effectively changing the electrical load seen by the PV array.
5. Maximum Power Point Identification
The system converges toward the voltage–current point that yields maximum power.
6. Continuous Tracking
This process repeats hundreds of times per second, enabling rapid response to environmental changes.
7. Common MPPT Algorithms
Perturb and Observe (P&O)
Widely used due to simplicity and robustness. It introduces small voltage perturbations and observes power changes, with minor oscillations near the maximum power point.
Incremental Conductance
Determines the maximum power point by comparing instantaneous conductance and its rate of change. It offers higher steady-state accuracy but requires faster and more precise sensing.
In modern hybrid MPPT solar inverters, MPPT operation is tightly coordinated with battery management systems and grid interaction logic to maintain overall system stability.
The electrical characteristics of PV modules are inherently nonlinear. For any given irradiance and temperature, there exists only one operating point at which power output is maximized.
Without MPPT:
The inverter operates at a fixed voltage
Shifts in environmental conditions move the true maximum power point
Significant energy losses occur
The primary functions of MPPT include:
Maximizing energy output from PV modules
Decoupling PV voltage from battery or DC bus voltage
Improving performance under partial shading and low-light conditions
Enhancing overall system efficiency and economic return
MPPT can be compared to an experienced mountain guide, continuously leading the system toward the peak of the power curve and maintaining operation at that peak as conditions change.
One MPPT input controlling all PV strings
Suitable for uniform roof orientation
Lower system cost
Independent tracking for different PV strings
Ideal for multiple roof directions or shading
Reduces mismatch losses
Dual MPPT inverters are strongly recommended for residential solar systems and commercial solar systems with complex layouts.
A dual MPPT inverter contains two independent MPPT channels.
This allows:
Different panel orientations (east–west, south–north)
Different panel models or string lengths
Higher system design flexibility
In practice, dual MPPT often delivers better energy yield than higher inverter wattage alone.
| Feature | MPPT | PWM |
|---|---|---|
| Energy efficiency | High | Low |
| Works with high-voltage arrays | Yes | No |
| Performance in weak sunlight | Excellent | Limited |
| System scalability | High | Low |
MPPT has become the industry standard for modern solar inverter systems.
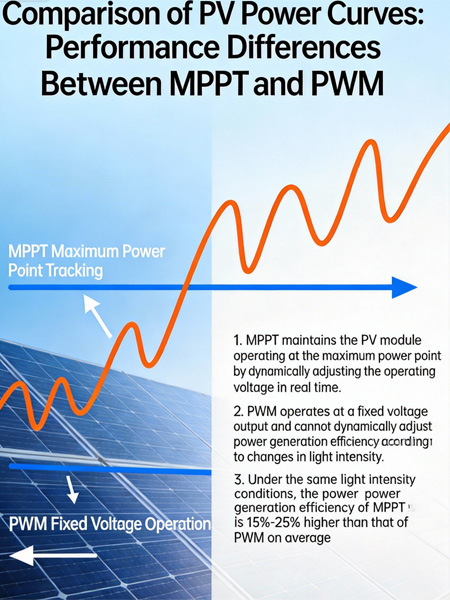
Comparison of PV power curves: performace differences between MPPT and PWM
More to read: https://www.anern.com/working-principle-of-pwm-and-mppt-solar-charge-controllers.html
| Aspect | High-Voltage MPPT | Low-Voltage MPPT |
| Current | Lower | Higher |
| Cable loss | Lower | Higher |
| Typical use | Residential & commercial | Small off-grid systems |
High-voltage MPPT systems generally provide better efficiency and scalability.
MPPT inverter pricing depends on:
Rated power
Number of MPPT channels
Hybrid or non-hybrid design
Battery compatibility
Although MPPT inverters cost more than basic alternatives, the increased energy yield usually shortens payback time.
Selecting an MPPT inverter is a system-level engineering decision, not a simple price comparison.
Key technical parameters include:
Rated AC power output
MPPT tracking efficiency (above 99% is considered excellent)
Maximum and European weighted efficiency
MPPT voltage operating range
Starting voltage
Number of independent MPPT channels
Environmental protection rating (e.g., IP65)
Proper alignment of these parameters ensures long-term system stability and optimal performance.
In practical projects, selecting an MPPT inverter is rarely about peak efficiency alone. System designers typically evaluate PV voltage range, MPPT channel count, battery compatibility, and grid stability as a whole.
For residential or small commercial energy storage systems, an MPPT hybrid inverter with a wide PV input range and dual MPPT channels allows flexible panel string design while maintaining stable battery charging. Compatibility with common lithium battery chemistries, such as LiFePO₄, is essential for long-term system reliability.
In regions with unstable or weak grids, installers often prioritize hybrid MPPT solar inverters capable of seamless grid–battery–solar coordination, rather than frequent mode switching. From a manufacturing perspective, stable MPPT algorithms, conservative thermal design, and long-term component durability tend to have a greater impact on system lifespan than marginal efficiency gains measured under laboratory conditions.
This system-oriented approach helps ensure consistent performance across diverse operating environments.
In many African countries, grid instability, frequent outages, and limited grid coverage make MPPT hybrid inverters a core infrastructure component rather than an optional upgrade.
Typical system priorities include:
Wide PV input voltage range to accommodate flexible string design
Strong battery–solar coordination for long backup durations
Stable MPPT performance under high temperatures and fluctuating irradiance
Hybrid MPPT solar inverters are commonly deployed in residential backup systems, telecom sites, clinics, and small commercial facilities where energy continuity is critical.

80 Sets of 10.2kW EVO Solar Inverters in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Middle East presents a different challenge profile: strong solar resources combined with extreme ambient temperatures.
In this region, MPPT inverter selection often focuses on:
Conservative thermal design and effective heat dissipation
MPPT algorithms that remain stable at high panel temperatures
Compatibility with higher-voltage PV strings to reduce cable losses
Well-designed MPPT hybrid inverters help maintain consistent performance and protect system components in desert and high-heat environments.

Example: MPPT inverter installation in Lebanon
Across Southeast Asia, rising electricity costs and mixed grid reliability drive demand for flexible hybrid MPPT inverter systems.
Key considerations include:
Dual MPPT inputs for complex rooftops and partial shading
Seamless switching between solar, battery, and grid sources
Optimized self-consumption to reduce peak electricity charges
MPPT hybrid inverters are widely used in residential and small commercial systems aiming to balance energy independence with cost efficiency.

Example: MPPT inverter in Myanmar
From a manufacturer's perspective, effective MPPT design depends on:
Wide and stable MPPT voltage range
Intelligent interaction with battery systems
Reliable performance in harsh environments
Anern focuses on system compatibility, long-term stability, and real-world grid conditions rather than lab-only efficiency numbers.
In most cases, yes.
Reasons include:
Higher daily energy output
Faster ROI
Better long-term system stability
For medium and large systems, MPPT is not an upgrade — it is a necessity.
A properly designed MPPT inverter does not damage batteries.
Battery issues usually result from:
Incorrect voltage configuration
Incompatible battery chemistry
Poor thermal management
Quality MPPT hybrid inverters include battery protection logic and communication protocols.
Typical lifespan:
10–15 years under normal conditions
Key durability factors:
Thermal design
Component quality
Algorithm stability
Solar Inverter Manufacturers focusing on long-term reliability prioritize stable tracking over aggressive tracking.
PV voltage outside MPPT range
Incorrect string configuration
Overheating due to poor ventilation
Most issues are system design or installation related, not MPPT technology itself.
Higher upfront cost, and more complex electronics. However, these disadvantages are usually outweighed by energy gains and system flexibility.
MPPT means Maximum Power Point Tracking, enabling an inverter to extract the maximum possible power from solar panels under varying conditions.
Dual MPPT inverters perform better in systems with multiple panel orientations or partial shading.
MPPT solar inverters form the technical foundation of modern solar power systems. Across grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid applications, a well-designed MPPT inverter delivers higher energy yield, improved system stability, and superior long-term economic performance. For projects operating under diverse environmental and grid conditions, selecting an experienced MPPT inverter manufacturer is a future-proof choice.
Recommended Readings: